Rewterz Threat Alert – North Korea Linked Konni APT Group – Active IOCs
July 31, 2023
Rewterz Threat Medium – IcedID Banking Trojan aka BokBot – Active IOCs
July 31, 2023
Rewterz Threat Alert – North Korea Linked Konni APT Group – Active IOCs
July 31, 2023
Rewterz Threat Medium – IcedID Banking Trojan aka BokBot – Active IOCs
July 31, 2023Severity
High
Analysis Summary
The Abyss Locker operation is a recent ransomware campaign that has developed a Linux encryptor specifically targeting VMware’s ESXi virtual machine platform in enterprise attacks. With businesses increasingly using virtual machines for resource management and disaster recovery, ransomware groups have started creating encryptors to exploit this platform.
VMware ESXi is a popular virtual machine platform, making it a prime target for ransomware gangs. Several other ransomware operations, including AvosLocker, Black Basta, BlackMatter, HelloKitty, LockBit, Luna, RansomEXX, REvil, and Royal.
Abyss Locker is a relatively new ransomware group that emerged in March 2023 and has been targeting companies in their attacks. Like other ransomware operations, Abyss Locker infiltrates corporate networks, exfiltrate data for double-extortion purposes, and then encrypts devices on the network.
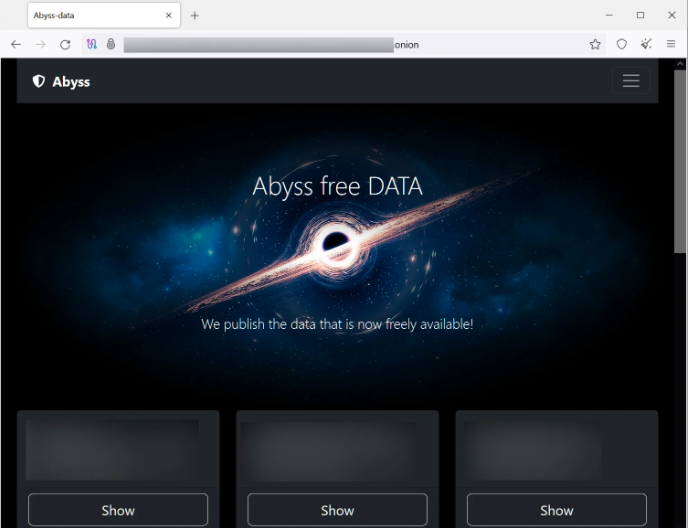
The stolen data is used as leverage to extort victims into paying the ransom, with the threat actors creating a Tor data leak site named ‘Abyss-data’ to list their fourteen victims. The ransomware group claims to have stolen varying amounts of data, ranging from 35 GB to as high as 700 GB.
Researchers first discovered a Linux ELF encryptor for the Abyss Locker operation, which specifically targets VMware ESXi servers. The encryptor utilizes the ‘esxcli’ command-line VMware ESXi management tool to list all available virtual machines and then forcibly shut them down using the ‘vm process kill’ command.
After terminating the virtual machines, Abyss Locker proceeds to encrypt all associated files, including virtual disks (.vmdk), metadata (.vmsd), and snapshots (.vmsn) with the ‘.crypt’ extension. Additionally, all other files on the affected device are encrypted, and a ransom note with a ‘.README_TO_RESTORE’ extension is created for each file. This ransom note provides information on the attack and contains a unique link to the threat actor’s Tor negotiation site for communication with the ransomware gang.
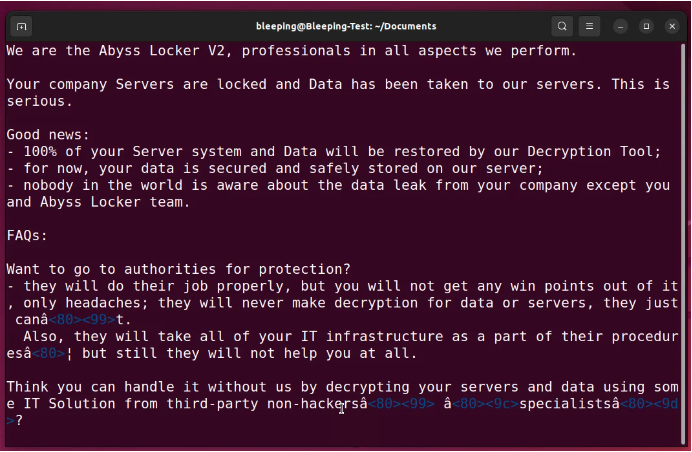
image source
Security experts, including Michael Gillespie, have noted that the Abyss Locker Linux encryptor appears to be based on the Hello Kitty ransomware. However, it remains unclear whether Abyss Locker is a rebrand of the HelloKitty operation or if another ransomware group gained access to the encryptor’s source code, as observed in cases like the Vice Society ransomware.
The sophistication and targeting of VMware ESXi virtual machines highlight the evolving nature of ransomware attacks, especially concerning virtualized environments. To mitigate the risks posed by such attacks, organizations must adopt robust cybersecurity measures, implement regular and secure data backups, and deploy proactive security strategies to defend against ransomware threats effectively.
Impact
- File Encryption
- Sensitive Information Theft
Remediation
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Maintain Offline Backups – In a ransomware attack, the adversary will often delete or encrypt backups if they have access to them. That’s why it’s important to keep offline (preferably off-site), encrypted backups of data and test them regularly.
- Regularly update all software, applications, and operating systems, including VMware ESXi, with the latest security patches and updates.
- Employ network segmentation to isolate critical systems, including VMware ESXi servers, from the rest of the network. Limit access to essential personnel only and use firewalls and security measures to prevent lateral movement within the network.
- Implement strong access controls, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least privilege principles. Limit administrative access to only those who require it and monitor privileged account activity closely.
- Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to detect and block ransomware and other malicious activities. These systems can help identify and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
- Install and maintain reputable endpoint protection and antivirus software on all devices.
- Implement continuous monitoring of network and system activity to identify unusual behavior, such as unauthorized access attempts or large data transfers.
- Employ robust email filtering and web security solutions to block malicious attachments and links, reducing the chances of phishing attacks and malware delivery.
- Develop a detailed incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in case of a ransomware attack.
- Conduct security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address weaknesses in the organization’s infrastructure and defenses.