Rewterz Threat Advisory – CVE-2023-35854 – Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus Vulnerability
June 21, 2023
Rewterz Threat Update – Update on Active Exploitation of Critical VMware Vulnerability
June 21, 2023
Rewterz Threat Advisory – CVE-2023-35854 – Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus Vulnerability
June 21, 2023
Rewterz Threat Update – Update on Active Exploitation of Critical VMware Vulnerability
June 21, 2023Severity
High
Analysis Summary
BlueNoroff is a sophisticated Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group that has been active since at least 2014. The group is believed to be based in North Korea and is linked to the Lazarus Group, another North Korean APT group. These threat actors are primarily focused on financial gain, with a particular emphasis on targeting banks and financial institutions. The group is known for using a variety of sophisticated techniques, including spear-phishing, malware, and network infiltration, to gain access to their targets.
One of this APT’s most notable attacks was the 2016 theft of $81 million from the Bangladesh Bank. The group also targeted various other banks and financial institutions in countries such as Mexico, Poland, and Vietnam.
The group has been known to use a variety of malware, including the Bankshot, Fallchill, and Hoplight families of malware. These tools are designed to provide the group with persistent access to targeted systems, allowing them to exfiltrate sensitive information and steal funds over an extended period.
BlueNoroff is believed to be closely linked to the North Korean government, and its activities are thought to be part of a broader state-sponsored cyber espionage and cybercrime campaign. The group is known for its sophisticated techniques and is considered to be one of the most significant threats to the financial sector.
In some attacks, BlueNoroff explores with more advanced adversary techniques to increase the effectiveness of bypassing Windows security capabilities and interrupting cyber defence operations.
Threat actors have been spotted utilizing numerous scripts, such as Visual Basic and Windows Batch, and applying ISO and VHD file types to spread infection. The group has taken use of image files to bypass the Windows MoTW flag and evade detection. The latter is a Windows security feature that alerts users when they attempt to open an unfamiliar or suspicious file obtained from the internet.
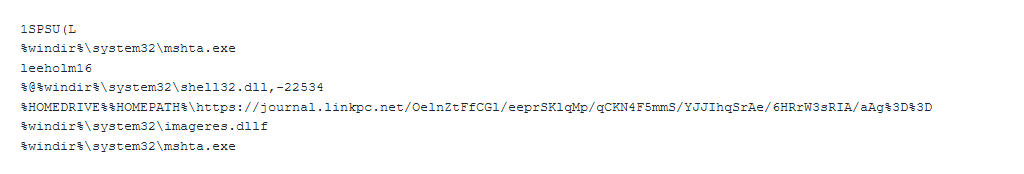
In the context of a recent BlueNoroff APT campaign, it has been reported that a file named “Password.txt.ln” is associated with their activities.
Impact
- Information Theft and Espionage
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- e5a6ddcc88c9abcce8774b4038974804
SHA-256
- d4b3086288f63489b27ebe487f872016af49a8779b53cd839c61ff2de52963b8
SHA-1
- d53a5dc6b050504d7599ba26a984bdd5bb9f23b5
URL
https://journal.linkpc.net/OelnZtFfCGl/eeprSKlqMp/qCKN4F5mmS/YJJIhqSrAe/6HRrW3sRIA/aAg==
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls
- Emails from unknown senders should always be treated with caution.
- Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Patch and upgrade any platforms and software timely and make it into a standard security policy. Prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities and zero-days.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions in a timely manner. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets