Rewterz Threat Alert – Modified Variant of BX Rat, JanelaRAT, Targeting Financial Institutions in LATAM – Active IOCs
August 25, 2023
Rewterz Threat Alert – Lazarus Group Deploys Stealthy QuiteRAT Malware via Zoho ManageEngine Flaw – Active IOCs
August 25, 2023
Rewterz Threat Alert – Modified Variant of BX Rat, JanelaRAT, Targeting Financial Institutions in LATAM – Active IOCs
August 25, 2023
Rewterz Threat Alert – Lazarus Group Deploys Stealthy QuiteRAT Malware via Zoho ManageEngine Flaw – Active IOCs
August 25, 2023Severity
High
Analysis Summary
REvil/Sodinokibi, also known as Sodin, is a sophisticated ransomware discovered in April 2019. This elusive malware encrypts files and cleverly erases its ransom request message, leaving victims unaware. Once encryption is complete, victims receive a Bitcoin ransom demand.
This ransomware evades traditional security measures, infiltrating systems undetected, appealing to cybercriminals due to its stealthy nature. It’s an example of Ransomware-as-a-Service, with code authors and affiliates working together. This model heightens its danger, enabling large-scale attacks with minimal risk.
REvil is linked to the GandCrab ransomware’s authors, who share connections. Globally, it targets organizations and individuals, concentrating on countries like Mexico, the U.S., Japan, and Germany. Notable attacks include JBS Foods, Kaseya, Travelex, and Acer, causing significant disruptions and financial losses.
REvil employs various attack methods, including RDP assaults, software flaws, and phishing. After infiltration, files and backups are encrypted. Sodinokibi ransomware can encrypt data using curve25519/Salsa20 and keys using curve25519/AES-256-CTR. The user’s private key is encrypted by the malware using two public keys. Additionally, this infection uses asymmetric key scheduling and command and control server obfuscation, which enable the malware to function without a connection to the C2.
In summary, REvil/Sodinokibi is a sophisticated ransomware with elusive behavior. It demands Bitcoin ransoms, exploits weaknesses, and poses a significant threat to organizations globally.
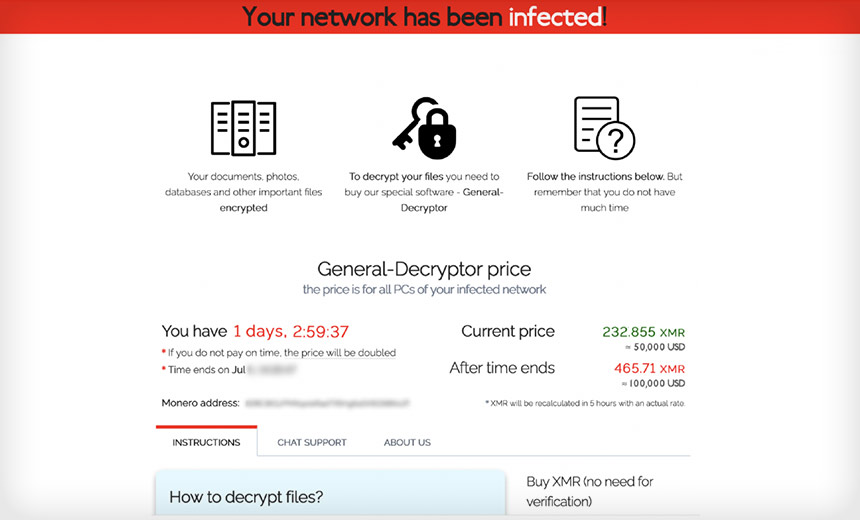
The ransom note placed by REvil (Source: Elliptic)
Impact
- File Encryption
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- ff1f6956f07e700a86b5986b63ea12db
- db2401798c8b41b0d5728e5b6bbb94cf
SHA-256
- 3e6fbc358e0204cb67a41b05771fac74f1b49737c7ab7138e415c7e9628ef545
- 861e2544ddb9739d79b265aab1e327d11617bc9d9c94bc5b35282c33fcb419bc
SHA-1
- a8d88813f2691cf71e8d6790e473593644c913ed
- 6620f5647a14e543d14d447ee2bd7fecc03be882
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls
- Maintain cyber hygiene by updating your anti-virus software and implementing a patch management lifecycle.
- Maintain Offline Backups – In a ransomware attack, the adversary will often delete or encrypt backups if they have access to them. That’s why it’s important to keep offline (preferably off-site), encrypted backups of data and test them regularly.
- Emails from unknown senders should always be treated with caution.
- Never trust or open links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders