Severity
High
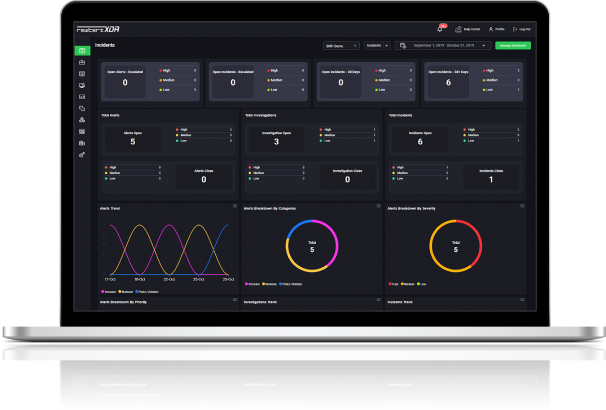
Analysis Summary
The Mirai botnet is a type of malware that infects Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as routers, security cameras, and other smart devices, in order to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. The botnet was first discovered in August 2016 and quickly gained notoriety for its ability to launch some of the largest DDoS attacks ever recorded, including an attack that took down the DNS provider Dyn.
Mirai works by scanning the internet for devices that use default or easily guessable passwords, such as “admin” or “password”. Once a vulnerable device is identified, the malware infects it and adds it to the botnet, which can then be used to launch DDoS attacks on a target.
Mirai is particularly effective because it is able to exploit the large number of poorly secured IoT devices that are connected to the internet. This makes it difficult to defend against, as many of these devices have limited processing power and memory, and may not receive regular security updates.
Since its discovery, Mirai has continued to evolve and new variants of the malware have been detected. The best defense against Mirai is to ensure that IoT devices are properly secured, with strong passwords and regular security updates. Network administrators can also use tools to monitor for unusual traffic patterns that may indicate a DDoS attack is underway.
Impact
- Server Outage
- Data Loss
- Website Downtime
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- b299422fb8c0c32842bfde2aa2a48c0e
- 5e0f69dd3ec722642f4f9fc00691fd50
- 92c726445f9550e9e390b248a5ca3b01
- 9d15b124fc21113edaa0ab73650ddc07
- 63009e75103d45ec08e091b9bfa65799
SHA-256
- e898d6916c5b09263a8b0cb2038aa0ac77a894a5af06cedb343f42966edae28c
- 897fcc1545e924eed74737927de213d0e29105dc6e52d44dfef6ca80eb5fa8e4
- ac286505cddd22ddf874957ee3c9eef971225ae183ba3246b07c22ecf1a641a9
- 221e9f87536e13734451ac154fcd0244606b441c6f18b078dfd1328f2dac9e7a
- 3cd6c368baa4454dd17d6d1c051a8e03c76ba3e7720d4cf830d9cc11fc48bb22
SHA-1
- 1b7ba985c673de623e8ac7ee67298d6c04d9ba4c
- f56f4fbdd652872c8b4cd9cb113f8ed91d7dc375
- bb0447c4aff6a638f04b61f5bcb57424fe1f1948
- bfe5fe8f83ab89f58dff97308a2c2deed21de13a
- 3edacda333a69015052591a492eed9e834703417
Remediation
- Upgrade your operating system.
- Don’t open files and links from unknown sources.
- Install and run anti-virus scans.