Severity
High
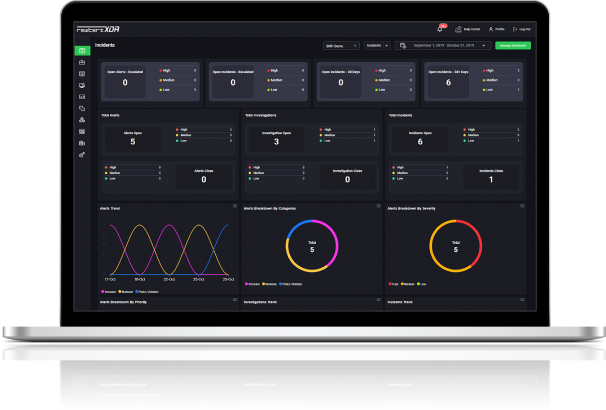
Analysis Summary
Tofsee malware has been around since 2016. Once installed on a compromised computer, it can be used to send spam emails and gather user data. The malware has the ability to download more modules to carry out different activities. It can track users’ online activities, steal personal information and credentials, and change browser and DNS settings. Tofsee has been known to spread through malicious email attachments, infected software downloads, and drive-by downloads from compromised websites. It can also persist on a system even after a reboot and can hide its presence from antivirus software. Upon execution, it drops multiple files onto the system and modifies the registry to ensure persistence. Tofsee uses a combination of stealth techniques to avoid detection, such as process hollowing, code obfuscation, and anti-debugging measures. This malware can cause major damage, such as financial loss and computer infections. It is used by cybercriminals to generate as much revenue as possible. The program is likely to install unintentionally, causing a slew of issues for both the system and other users. Tofsee is also capable of injecting unwanted advertisements into web pages visited by the infected user and redirecting browser traffic to malicious websites.
In terms of mitigation, it is crucial to keep software and operating systems up to date, avoid downloading suspicious files, and use a reputable antivirus program.
Impact
- Information Theft
- Credential Theft
- Crypto-Mining
Indicators of Compromise
MD5
- 2cf91981ca2e2d726c32543af6417d17
- a28c8eef1dde99e1c5eb5c165931a391
- d7ce6eb241c8d1ceb14b3d112c8f4a78
- 4c9908656905016acaf1ba84d0b38ba6
- 3ce9c20950f4c88365f5b00821fb82bc
- cb9e877002111c6a01bf2a7c52071e94
SHA-256
- 163f70c5a5a9c266a470da5b913cc415aa829f96551010becb297b0519553c60
- cc5fb1d3eb7c98e5917b9938d48201f4fb505692f36548c55ca6a8760bd9b9d5
- 379c4cc1f342db17d4ce12d23b5c5ec7927cc6b8b7ffdbe94dea4d05d87249b0
- 658849d3fcdecf3a960c712819bc8e2eca2e0b53e6313e77edd3410dfd2468e8
- d39ae2052fefa45cbbd4a79e787b7e8b5821b6dc85e51760b0fdd8d6e0e24569
- 9bb2e96507b9b41d965d2d427497b54fb3eb90ef95fe2bc292175178851bbc4f
SHA-1
- b5176726712d6c3c3984bd273777a047334fe89a
- 04a4079fcd47a77d9f24b68c4c7f08f37eeab0ee
- 6b69360a095bf4066a9c063909cb4085d28843cc
- a9b3f47da19f997a6605a7206a5945bdb27fb7d1
- 24cf02e964179a1675e7eac602beb6794f972c9d
- 2618e2cff44e484ff5e7197e1b03455f149f4e0f
Remediation
- Block all threat indicators at your respective controls.
- Search for Indicators of compromise (IOCs) in your environment utilizing your respective security controls
- Emails from unknown senders should always be treated with caution.
- Never trust or open ” links and attachments received from unknown sources/senders.
- Patch and upgrade any platforms and software timely and make it into a standard security policy. Prioritize patching known exploited vulnerabilities and zero-days.
- Enable two-factor authentication.
- Enable antivirus and anti-malware software and update signature definitions in a timely manner. Using multi-layered protection is necessary to secure vulnerable assets